Authors
Authors
Read time: 8 minutes
With the recent proliferation of headlines around generative artificial intelligence (AI) and its potential for dramatic disruption, it’s easy to forget that the idea of machines being able to learn and interact dates back almost 75 years. Historians may disagree about exactly when generative AI became an active area of research, but many see Joseph Weizenbaum's development of the chatbot ELIZA at MIT in the 1960s as one of the first examples of a simulated conversation between a human user and a machine. Contrary to what the headlines may suggest, AI is by no means a new phenomenon.
Today, particularly after the release of consumer-facing technologies such as MidJourney, Dall-E 2, Imagen, Stability AI’s Stable Diffusion and, of course, OpenAI’s ChatGPT, we are on the cusp of the next exciting phase of the technological revolution. From the humble chatbot to the mighty machine learning algorithm that creates new content, AI is transforming how the entertainment business operates. It will soon become a business imperative for media companies.
In this guide, which represents the time and investment of many hundreds of human lawyer hours, we'll explore how the law views the use of AI in the media sector. We’ll address the key developments that have shaped the law concerning AI in the last few years, from the development of new regulations to real-world examples of the technology being legally disruptive in the sector.
Introduction
We are mindful when describing the impact of AI on media and entertainment, as with many other sectors, of the ethical implications associated with its use – not least, the potential impact on human creative industries, as well as bias and privacy concerns. And as we mentioned in our Guide to the Metaverse, although the entertainment sector is often at the forefront of the development of machine learning, other sectors are close behind.
We hope the information and examples we share throughout this guide will help our readers prepare for the changes that AI will bring to the creative industries and understand how the law will play a part.
How does AI work?
In simple terms, AI systems are designed to process and interpret huge scores of data, recognize repeating patterns within that data, and then produce an output. In a sense, this process is not so different from the ways in which the human brain works, but with computational muscle behind it all. Fundamental to the AI process are the concepts of machine learning and neural networks. Machine learning enables systems to improve performance over time without the requirement for explicit programming. Neural networks are computational models inspired by the structure and functioning of the human brain. They consist of interconnected nodes, or artificial neurons, that process and transmit information. AI systems operate by combining these techniques to provide intelligent solutions in a range of applications.
AI comes in a number of different forms, each with its own strengths and weaknesses, for use in different applications and domains. In the world of media and entertainment, AI is used in countless applications including by far its most controversial application: to generate synthetic content.
The impact of AI on the creative industries
AI has already started reshaping society and continues to do so at an accelerating pace. Within the creative industries, the potential impact of AI is vast and rapidly evolving. The market value of AI in media and entertainment is projected to reach close to $100 billion in the next seven years. This surge in value stems from the industry’s ability to leverage AI to engage audiences through innovative means, particularly at a time when consumers are bombarded with an overwhelming volume of content.
Notably, major technology companies and media conglomerates have been investing in AI on a huge scale. AI powers recommendation systems, editing tools and filtering mechanisms; but no AI system has caused a more significant wave of emotion through the entertainment sector than “generative AI,” a term used to describe AI systems that are designed to create new information such as text, images, music or footage based on the data on which they were trained. Generative AI produces outputs of ‘synthetic’ content based on a set of input parameters often referred to as “prompts” and its potential to disrupt the content industries is fueling heated controversies around the globe.
First, let’s address the image sector. During the course of 2022, a number of AI-powered image-generation services were released to the public (Dall-E, MidJourney, Stable Diffusion), causing a wave of enthusiasm and angst in equal measures within the artistic community. What happened next will be remembered in the AI history books, as the moment “the penny dropped” for the content industries, and came in the form of two lawsuits from Getty Images against Stability AI claiming Stability AI unlawfully copied and processed millions of images protected by copyright and the associated metadata owned or represented by Getty Images without a license. Amidst the commotion that followed, few will remember that Getty, unlike others in the creative sector, is not actually arguing against the development of image generation services, but against the practice of training them without a license, especially where Getty Images provides viable licensing options to do so. As they became public, these cases immediately captured the imagination of the entire creative sector and it is difficult to overstate the importance that these cases are likely to have on the future of the creative sector. This guide will explore these topics in details.
Fast forward to 2023 and the music industry is on the spot. AI-generated songs replicating the styles of popular artists like Ye, Eminem and Ariana Grande have emerged, leading to allegations of industrial-scale copyright violations and clashes between user-upload platforms and record labels. Advanced AI music generators, such as Jukebox by OpenAI and MusicLM by Google, are said to have been trained on massive datasets of music, raising questions about the balance between innovation and authenticity. While AI opens new creative horizons for musicians, it challenges the traditional concepts of creativity, composition and human production.
In film and TV, concerns have arisen regarding the role of writers, leading to strikes by organizations like the Writers Guild of America, as AI-powered scriptwriting tools offer new possibilities while challenging the unique creative touch of human storytellers. The underlying sentiment is clear from those who may be concerned about becoming expendable.
In the realm of social media, AI is used to combat hate speech by filtering and identifying abusive content. Facial recognition and AI algorithms power popular filters on platforms like TikTok, Instagram and Snapchat. Snapchat’s “My AI” chatbot, powered by ChatGPT, has opened new avenues for user engagement, offering personalized recommendations and participating in conversations. AI has transformed social media, empowering users to express themselves creatively and connect with others in novel ways. Equally, AI can be a negative influence, allowing intrusion, deception, fraud, false positives and, of course, fake news.
AI is an exhilarating technological catalyst and a game changer for the entire creative sector. The impact of the technology can hardly be understated as it transforms the way content is created, distributed and consumed. Used as a tool to enhance creativity, AI has the power to remove barriers to artistic creation and propel a whole new generation of creators to the fore. Into the wrong hands however, AI can cause formidable disruption.
The legal issues
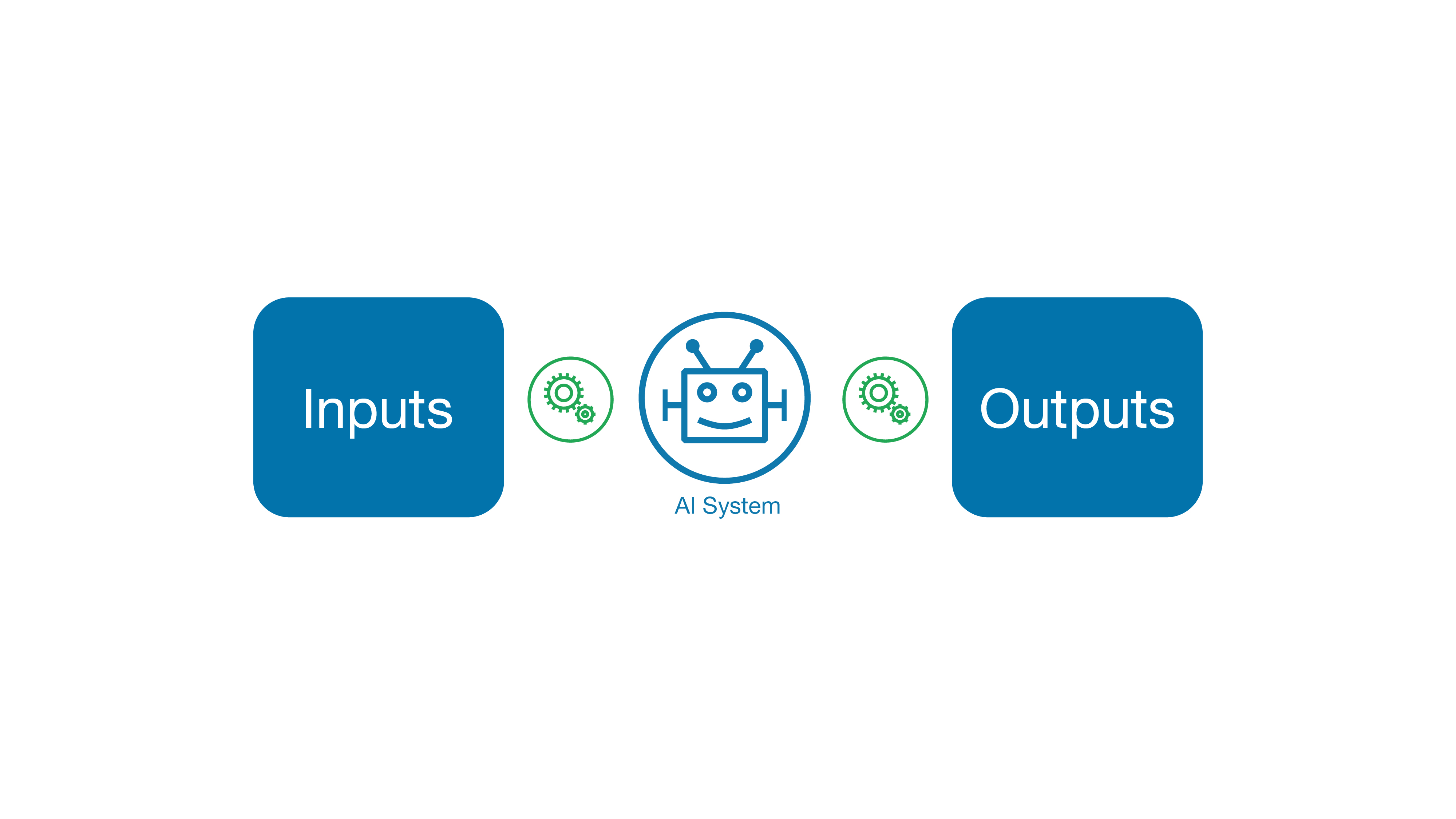
The image below shows how the legal issues arising with respect to AI systems fall into three categories: input, system, output:
- The input stage refers to an AI system development stage and encompasses all the steps that are needed to obtain a system performing according to its desired capabilities. Importantly, this is the stage during which an AI system will be fed ‘input data’ – in vast quantities – to learn from.
- The system refers to the algorithm, the model, the code and generally how the system has been programed.
- The output stage, finally, designates all that is being produced and generated by the AI system, once ready and released.
The above image shows a blue box on the left and on the right of the page, they are both the same in size and color. In the middle of those boxes is a robot image. The word ‘Inputs’ is written in the left hand box. And in the right hand box is the word ‘Outputs’. Under the robot image in the middle, the words ‘AI System’ is written. In between the left hand box and the robot image and the right hand box there are 2 cogs to infer motion.
Each category carries its own load of legal issues and legal risks that this guide will explore in details, through the prism of both existing and future legislation. For once, the law, at least parts of it, does not appear to be entirely ‘lagging behind’ the technology and whilst the sector may want in experience and practice, it is interesting to see how certain long-held debates, including on text and data mining (TDM), are resurfacing with a fresh outlook.
AI regulation, on the other hand, is in its infancy and the writers of this guide are well aware that law-making in the field of AI is unfolding as we write. We will be commenting, where relevant, on the various initiatives but we are conscious that it is early, and we will therefore revisit this guide periodically to keep up with the legal framework for AI as it develops.
As we delve into the intricacies of AI, this Guide aims to explore its diverse applications in the entertainment and media sector, discuss legal frameworks in which it currently exists and equip you with the knowledge to navigate the ever-evolving landscape of AI technologies and their impact on our lives and businesses.
Authors